Monitoring irrigation water between coral reefs
The coral island of Lifou is a dream island in the archipelago of New Caledonia, a French overseas territory in the heart of the Pacific Ocean. It is a luxuriant island, a destination for lovers of the sea and snorkeling, where it is possible to come into contact with the traditional customs and traditions of the Kanak tribes. It has a population of 21,000 inhabitants and covers an area of 1150 km2, making it the largest of the Loyalty Islands.
Lifou offers breathtaking views, pristine white sandy beaches, and sheer cliffs. Thanks to the favorable climate in Lifou, typical fruits such as the Pogo banana, lychee, papaya, coconut, and many other delicacies are grown in abundance. These crops require continuous irrigation and technological systems to manage and monitor the pumping stations for agricultural water to irrigate the numerous orchards.
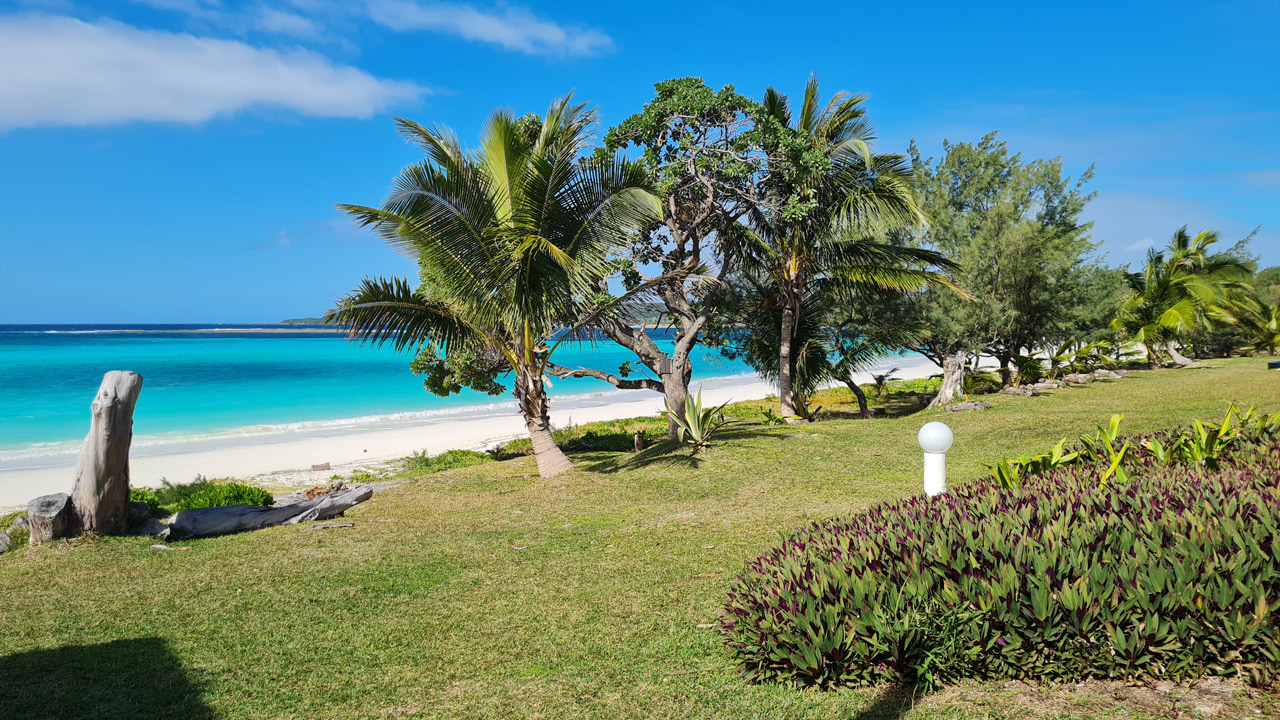

image 1 - a simplified image of the coastline and type of crops
The monitoring system of the pumping stations
Therefore, it was necessary to implement a monitoring system for these stations, collecting planting data from 10 stations across the Loyalty Islands archipelago and 47 across New Caledonia. In turn, the data is sent directly to the Cloud via the MQTT protocol, a simple and lightweight protocol for exchanging messages that require few device resources to manage it. This means significant time savings during the configuration and installation phase and no need to use dedicated programming languages or complex supervision systems. The objective achieved is threefold: detection of leaks, monitoring of water consumption according to the operating time of the users, and general monitoring of the system to schedule maintenance or replacement of components before any faults occur.
This technological innovation initiative has been implemented by the Pacific Community, in collaboration with the provinces and the government of New Caledonia, under the project “PROTEGE" funded by the European Union.
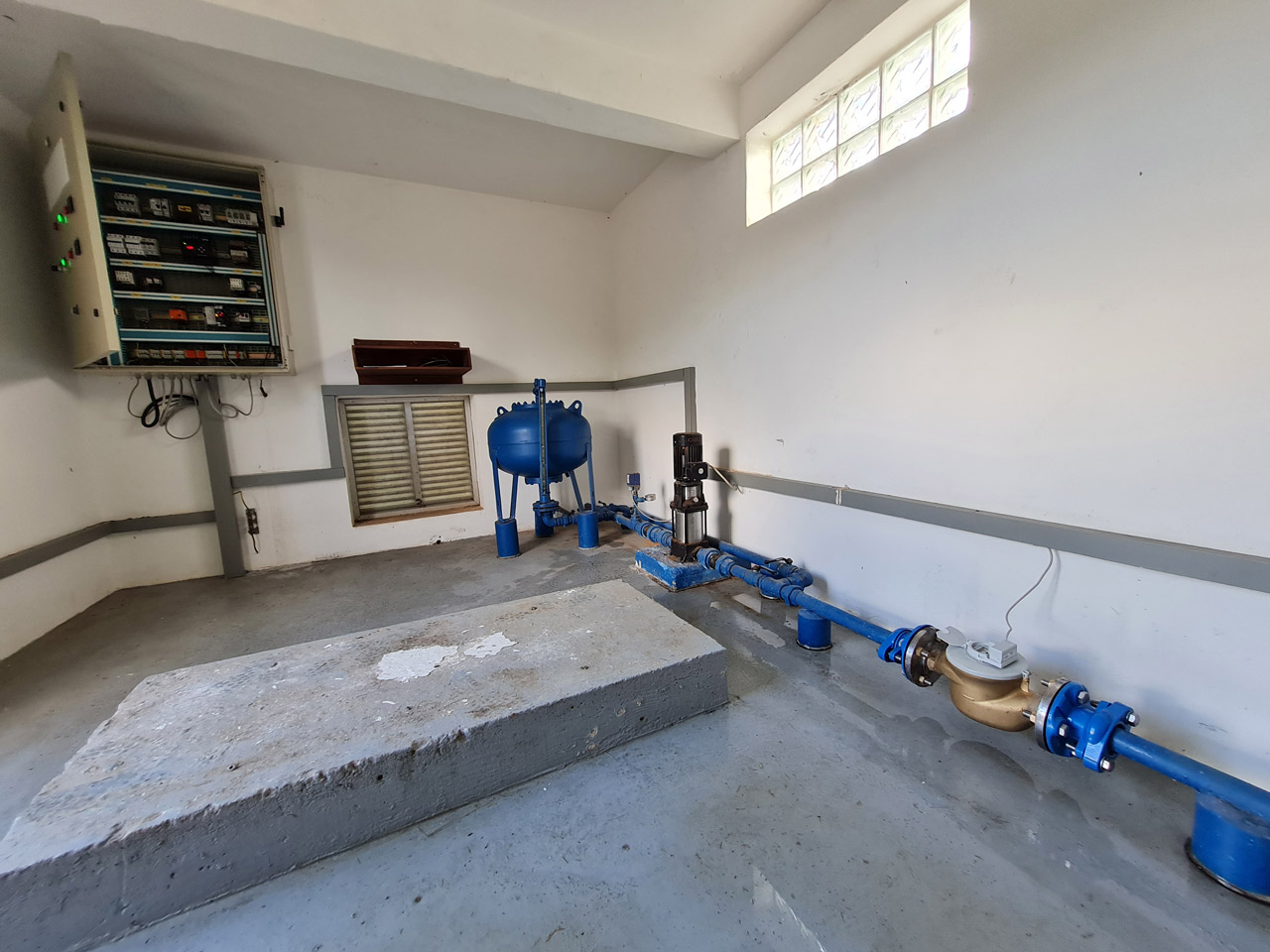

image 2 - one of 47 pumping stations all managed with the SENECA monitoring system
The key role of SENECA Z-LTE datalogger
The data collection and transmission system is the advanced Z-LTE datalogger, a SENECA device which, thanks to enhanced industrialization and a high-performance 4G/LTE modem with GPS GNSS receiver up to 55 channels, can respond to the growing need for real-time analysis and integration with IT systems. Z-LTE is used to monitor the electrical parameters of the pumping station, the water consumption by measuring the pulses coming from the water meters, and the correct functioning of the pressurization units. The SENECA datalogger is powered by a UPS with an external battery and the ability to monitor the charge level and battery status.
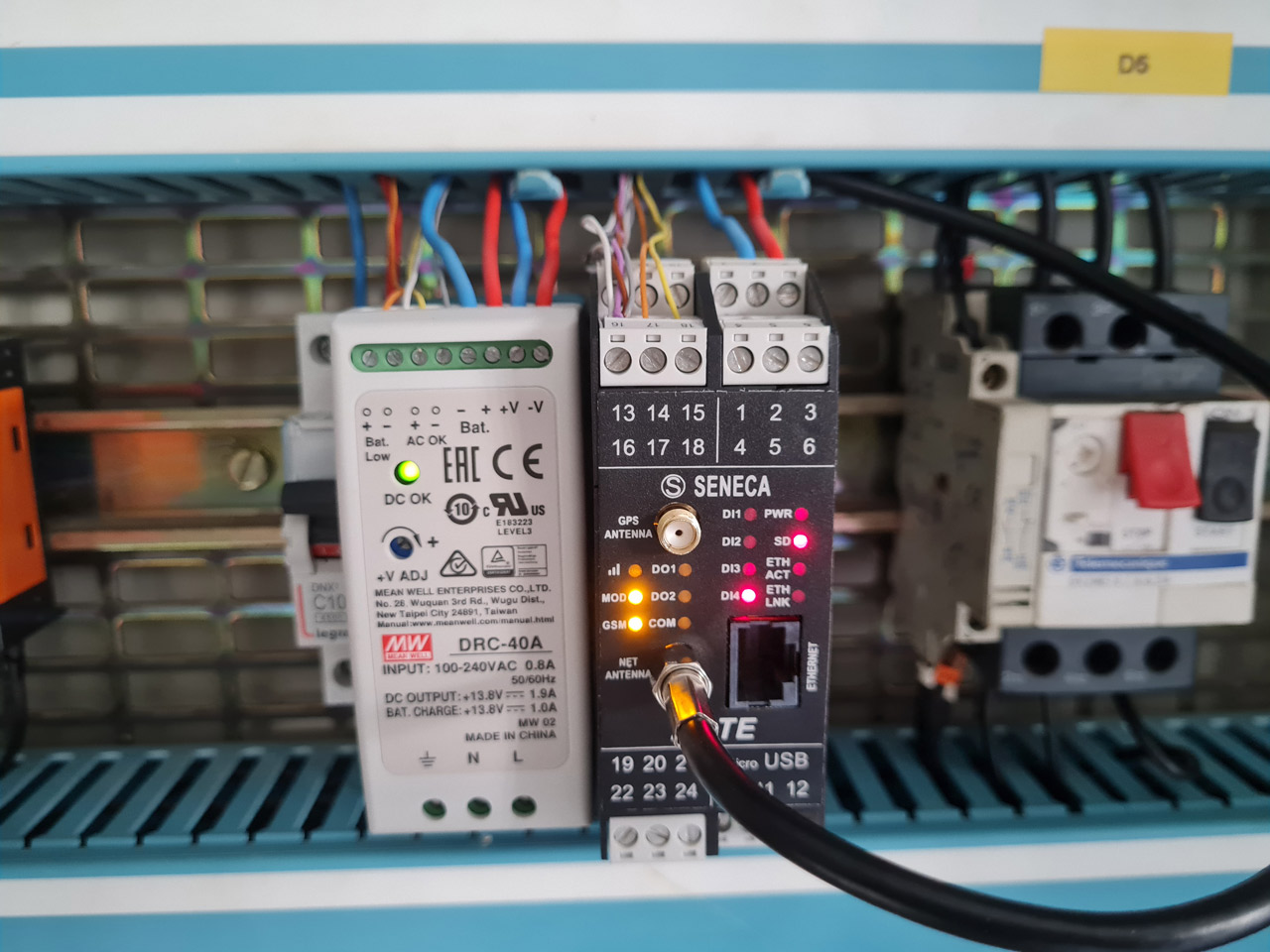

image 3 - Detail image of the SENECA Z-LTE data logger during the correct operation

 ES
ES